- 24*7 Assistance / Whatsapp
- (+91) 833 7040 362
- care@prostatesurgeryindia.com
- prostatesurgeryindia@gmail.com
Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy - Prostate Surgery India
- Home
- Procedures
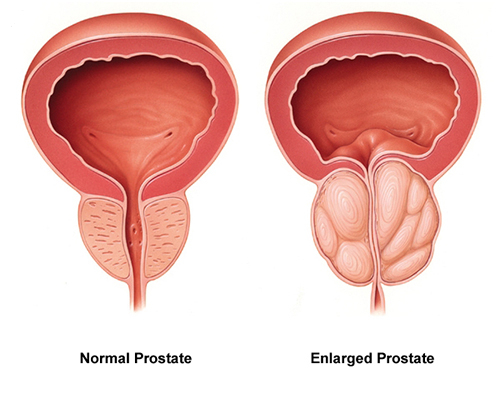
- Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
The surgery involves making several small (1-1.5 cm) incisions in the abdomen rather than an abdominal incision like in open radical prostatectomy. These small incisions provide access to the prostate gland. Operating tools, cameras, and other instruments are then inserted into the body. The surgeon then uses these tools to remove the prostate gland and nearby lymph nodes.
By using a tiny camera, the surgeon can have a magnified view inside the abdominal cavity. The surgeon will then seal the cuts or suture them with absorbent materials. In some cases, a small tube called a urinary catheter may be inserted and left in place for a few days or weeks.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy:
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy is a minimally invasive surgery that is used to remove the prostate gland. It is performed through several small incisions in the abdomen, rather than a single large incision. This can lead to a number of advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
Advantages of Lap. Radical Prostatectomy Include:
- Reduced Risk of Blood Loss
- Proven Long-Term Survival Benefit
- Minimal Scarring
- Lower Risk of Urinary Incontinence
- Reduced Postoperative Pain
- Faster Recovery
- Eliminating Any Possible Cancer from the Region
Recovery After Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
Recovery following a Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy is usually shorter than recovery after traditional open surgery. Most patients can resume their normal activities within 1-2 weeks following the procedure, although strenuous physical activity may take longer to resume.
Patients will typically be wearing a urinary catheter for several days to help with urination. It is important to increase fluid intake and follow the post-operative instructions carefully.
Patients may be prescribed medication to help with pain and swelling. It is important to follow aftercare instructions to minimize any risks of infection. Regular check-ups with the doctor are recommended following the procedure to monitor progress and recovery.
Pre-Admission Testing:
Before a laparoscopic radical prostatectomy, your doctor will likely order a number of tests to assess your overall health and to make sure that you are a good candidate for the surgery. These tests may include:

This is a physical exam to examine the rectum and prostate and check for any abnormalities.
This test measures the amount of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in the blood. The PSA may be higher in individuals with prostate cancer and other prostate diseases.
A non-invasive imaging test which uses sound waves to create images of the prostate. It can help to identify any tumors or other abnormalities within the prostate.
This test examines a person’s urine to check for signs of infection or other problems. It is often used to detect urinary tract infections, kidney problems, and bladder cancer.
This test takes samples of urine and looks for bacteria and other organisms. It can be used to diagnose urinary tract infections.
This procedure takes a sample of tissue from the prostate to examine for signs of cancer and other conditions. It usually involves the use of a thin needle which is inserted through the rectum into the prostate.








