- 24*7 Assistance / Whatsapp
- (+91) 833 7040 362
- care@prostatesurgeryindia.com
- prostatesurgeryindia@gmail.com
TURP Prostate Surgery - Prostate Surgery India
- Home
- Procedures
- TURP Prostate Surgery
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) Surgery
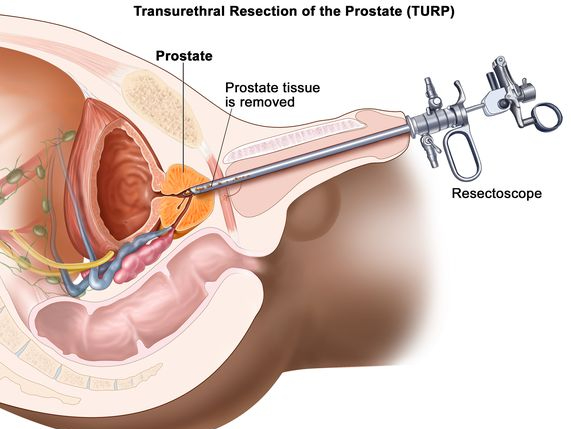
The procedure may be done under general anesthesia, or with a spinal or epidural anesthesia combined with local anesthesia. During the procedure, the surgeon will insert a resectoscope through the urethra and into the prostate. The resectoscope contains a metal loop that is used to cut away excess tissue. The pieces of tissue will be removed and analyzed for cancerous cells. The entire procedure usually takes about 1 to 2 hours.
Following TURP surgery, patients may experience some side effects such as blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pain with urination. These symptoms should improve over time. It is important to remember that the procedure does not cure BPH, but it can help to reduce the size of the prostate and improve urinary symptoms.
Advantages of TURP Surgery:
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure to remove tissue from the prostate gland. It is a common treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition in which the prostate gland enlarges and blocks the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
Advantages of TURP Surgery includes:
- Treatment of Severe BPH Symptoms
- Shorter Hospital Stay
- Low Risk of Complications
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure
Recovery After TURP Surgery:
Recovery from Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) surgery is typically smooth and uneventful. Most patients are able to go home on the same day as surgery. There are a few other things to keep in mind during your recovery from TURP surgery.
Catheter Use: You will need to wear a catheter for the first few days after surgery. This will help to drain urine from your bladder and prevent infection.
Drink Plenty of Fluids: You will need to drink plenty of fluids. This will help to flush out any blood or debris from your urinary tract.
Avoid Strenuous Activity: You should avoid lifting heavy objects and strenuous activity for at least two weeks after surgery.
Doctor's Advice: You should follow your doctor's instructions carefully. This will help to ensure a smooth and uneventful recovery.
Pre-Admission Testing:
There are a number of tests that your doctor may order before you have a TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate) surgery. These tests are done to assess your overall health and to make sure that you are a good candidate for surgery.

Your doctor will order a complete blood count (CBC), a blood chemistry panel, and a coagulation profile. These tests will check your blood for anaemia, infection, and any problems with your blood clotting.
Your doctor will collect a sample of your urine to check for infection or other problems.
The PSA test measures the amount of PSA in your blood. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate gland. A high PSA level can be a sign of prostate cancer, but it can also be caused by other conditions, such as BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
The DRE is a physical exam of the prostate gland. During the DRE, your doctor will insert a lubricated finger into your rectum to feel the size, shape, and consistency of your prostate gland.
The TRUS is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of the prostate gland. The TRUS can be used to measure the size of the prostate gland and to look for any abnormalities.








