- 24*7 Assistance / Whatsapp
- (+91) 833 7040 362
- care@prostatesurgeryindia.com
- prostatesurgeryindia@gmail.com
Robotic Prostatectomy Surgery - Prostate Surgery India
- Home
- Procedures
- Robotic Prostatectomy Surgery
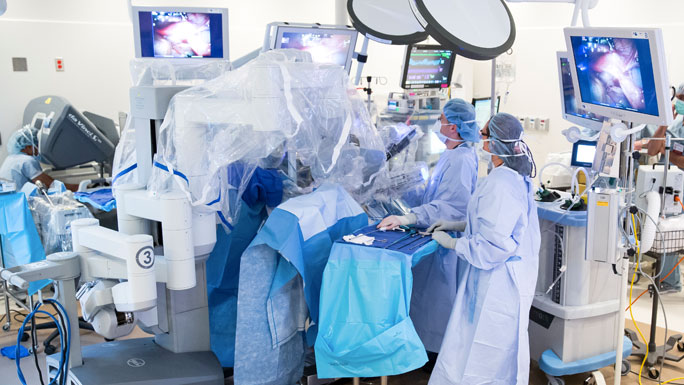
Robotic Prostatectomy
The robotic system consists of three robotic arms, each with a camera, a light source, and surgical instruments. The surgeon operates the robot from a console in the operating room, controlling the arms and instruments with the use of a joystick.
Robotic prostate surgery is typically used to remove the entire prostate gland to remove any cancerous tissue. It has become increasingly popular as it produces better outcomes than traditional open surgery, with fewer side effects and a shorter recovery time.
Advantages of Robotic Prostatectomy:
Robotic prostatectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is used to treat prostate cancer. The robotic system provides surgeons with a magnified, 3-D view of the prostate gland, which allows them to perform the surgery with greater precision and control.
Advantages of Robotic Prostatectomy Include:
- Less Blood Loss
- Less Pain
- Shorter Hospital Stay
- Faster Recovery
- Better Outcomes
- Superior Cancer Control
- Nerve Sparing
Recovery After Robotic Prostatectomy:
Recovery after robotic prostatectomy varies from person to person, but most patients can expect to make a full recovery within a few weeks. Here are some things you can expect during your recovery:
In the Hospital: You will likely stay in the hospital for one to two days after your surgery. During this time, you will be monitored for any complications and given pain medication as needed. You will also be taught how to care for your incisions and manage any other symptoms.
At Home: Once you are discharged from the hospital, you will need to rest for a few days. You should avoid lifting anything heavy, strenuous activity, and driving until your doctor approves of the same. You may also experience some bleeding, swelling, and pain at the incision sites. This is normal and should gradually improve over time.
Long-Term Recovery: Most men make a full recovery from robotic prostatectomy within a few weeks. However, some men may experience long-term side effects, such as incontinence and erectile dysfunction. These side effects are usually treatable, but they can take time to improve.
Pre-Admission Testing:
The tests required before robotic prostatectomy can vary depending on your individual medical history and the specific details of your surgery. However, few common tests that may be required include:
During this examination, your doctor will measure your height and weight, take your pulse and blood pressure, check your abdomen, the area between your testicles and anus, and the area that contains your bladder and prostate gland.
This blood test measures the level of PSA in your body. PSA is a substance produced by your prostate. Higher-than-normal levels may indicate prostate cancer.
Urine tests are used to check for infection and to assess your kidney function.
Imaging tests, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI, may be used to get a better look at your prostate gland and to plan the surgery.
This imaging test uses sound waves to create a picture of the prostate and any suspicious growths.
If your PSA levels are elevated or an abnormality is detected, a biopsy may be needed. During this test, a sample of prostate tissue will be removed and analyzed for signs of cancer.








